Redisson延迟队列是怎么搞的?
昨天,记录了Spring Boot基于Redisson实现订单状态延迟处理的思路后,就想着,还是要去搞清楚RedissonDelayedQueue的实现思路,所以,今天就忙里偷闲,去Github下载Redisson源码来大概查略一番。
如何创建RedissonDelayedQueue队列
在Test中,可以看到这样一段代码
1 | RBlockingQueue<Integer> queue1 = redisson.getBlockingQueue("test"); //按名称获取一个阻塞队列实例 |
在获取DelayedQueue队列时,会初始化两个队列名称redisson_delay_queue_{队列名}和redisson_delay_queue_timeout_{队列名},还会创建一个QueueTransferTask队列中转的定时任务,
添加队列
1 | dealyedQueue.offer(3, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //第一次参数是要发送给队列的数据,第二个参数是要延迟的时间,第三个参数是延迟的时间单位 |
这里,我们直接来到offerAsync方法
1 | public RFuture<Void> offerAsync(V e, long delay, TimeUnit timeUnit) { |
在代码中,我们可以看到,最终执行的Lua脚本,其他的代码基本是一目了然,我们主要来分析一下这段Lua脚本,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7local value = struct.pack('dLc0', tonumber(ARGV[2]), string.len(ARGV[3]), ARGV[3]); //将超时时间、随机Id和消息内容序列化为二进制
redis.call('zadd', KEYS[2], ARGV[1], value); //将序列化后的二进制内容按超时时间作为`score`存放到`redisson_delay_queue_timeout_{队列名}`这个有序集合(sorted set)中
redis.call('rpush', KEYS[3], value); //将序列化后的二进制内容添加到`redisson_delay_queue_{队列名}`列表(List)中
local v = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[2], 0, 0); //取出有序集合中的第一个元素
if v[1] == value then
redis.call('publish', KEYS[4], ARGV[1]); //如果取到第一个元素,则`publish`到`channel`中
end;
当publish到channel中,此时会触发onSubscribe然后执行pushTask方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15RFuture<Long> startTimeFuture = pushTaskAsync(); //执行`pushTaskAsync`方法,并返回到期时间
startTimeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
if (e instanceof RedissonShutdownException) {
return;
}
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
scheduleTask(System.currentTimeMillis() + 5 * 1000L);
return;
}
if (res != null) { //取到延迟时间,设置执行时间,到期时便去执行`pushTaskAsync`方法
scheduleTask(res);
}
});
我们继续来看pushTaskAsync方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20protected RFuture<Long> pushTaskAsync() {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG,
"local expiredValues = redis.call('zrangebyscore', KEYS[2], 0, ARGV[1], 'limit', 0, ARGV[2]); "
+ "if #expiredValues > 0 then "
+ "for i, v in ipairs(expiredValues) do "
+ "local randomId, value = struct.unpack('dLc0', v);"
+ "redis.call('rpush', KEYS[1], value);"
+ "redis.call('lrem', KEYS[3], 1, v);"
+ "end; "
+ "redis.call('zrem', KEYS[2], unpack(expiredValues));"
+ "end; "
// get startTime from scheduler queue head task
+ "local v = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[2], 0, 0, 'WITHSCORES'); "
+ "if v[1] ~= nil then "
+ "return v[2]; "
+ "end "
+ "return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getRawName(), timeoutSetName, queueName),
System.currentTimeMillis(), 100);
}
这里,我们依然只看Lua脚本这部分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 local expiredValues = redis.call('zrangebyscore', KEYS[2], 0, ARGV[1], 'limit', 0, ARGV[2]); //取出`redisson_delay_queue_timeout_{队列名}`中,分数小于当前时间戳的100条数据,意思就是取出到达延迟时间的数据
if #expiredValues > 0 then //如果有到期数据
for i, v in ipairs(expiredValues) do
local randomId, value = struct.unpack('dLc0', v); //将二进制反序列化
redis.call('rpush', KEYS[1], value); //将反序列化后的数据放入到`队列名`中的集合(List)中
redis.call('lrem', KEYS[3], 1, v); //将数据从`redisson_delay_queue_{队列名}`中移除掉
end;
redis.call('zrem', KEYS[2], unpack(expiredValues)); //批量删除`redisson_delay_queue_timeout_{队列名}`有序集合中的数据
end;
local v = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[2], 0, 0, 'WITHSCORES'); //取出`redisson_delay_queue_timeout_{队列名}`中最小分数即到期时间,作为定时任务参数,以便下次执行
if v[1] ~= nil then
return v[2];
end
return nil;
队列取出数据
这时候,我们取数据,就需要通过RBlockingQueue实例来取
1 | queue1.poll() |
我们来看看RBlockingQueue中的pollAsync方法
1 | public RFuture<V> pollAsync(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) { |
假巴意思总结一下
这里,我们大概来总结一下,大致的流程是消息生产端给Redis添加延迟消息时,会生成一个有序集合和列表,此时会触发QueueTransferTask这个定时任务,该类会执行pushTask方法设置延迟时间,到达延迟时间后,会再次执行pushTaskAsync方法,把临时队列中的数据添加到最终集合中去。生产端到最终集合队列中去取消息。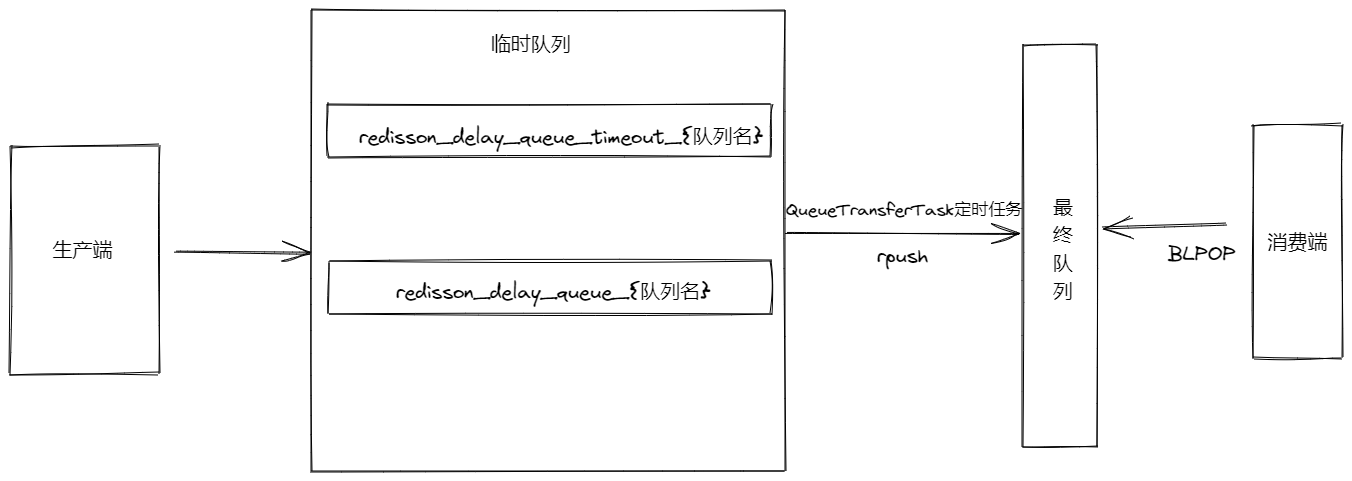
就先看这么多吧,其他细节以后再抽时间来学习。大概意思就是这么个意思,我也不知道对不对,反正先记下来。
Redisson延迟队列是怎么搞的?